Additionally, with recent technological advancements, more companies are utilizing predictive maintenance. However, to optimize maintenance costs, it is essential to learn from reactive maintenance and promote efficient and effective maintenance activities.
In this article, I will provide an overview of equipment maintenance and focus on what is necessary to reduce equipment failures.
1.Overview of Equipment Maintenance
Equipment maintenance is an essential activity to prevent machinery and equipment failures and to maintain their functionality. The goal is to reduce unexpected failures, extend the lifespan of equipment, and minimize the lifecycle cost (LCC).
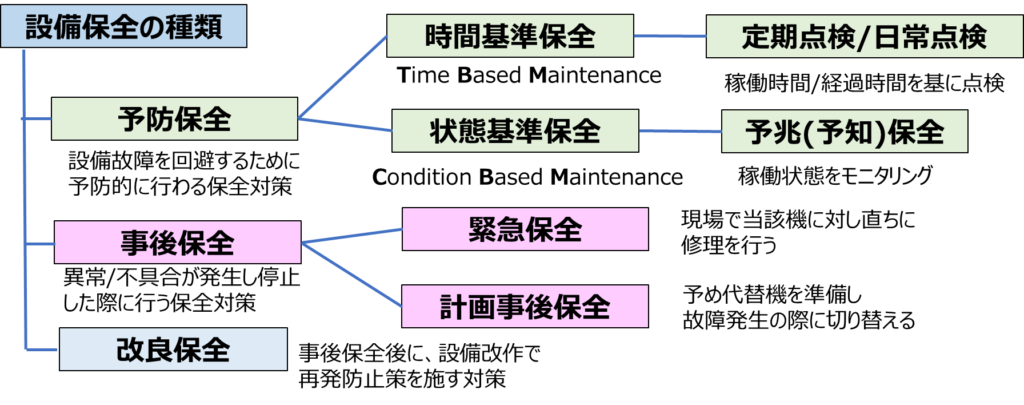
Equipment maintenance can be broadly classified into the following types
(1)Preventive Maintenance: Inspections and part replacements are carried out based on the operating time or elapsed time of machinery to prevent problems before they occur.
・Time-Based Maintenance: Inspections and maintenance are performed at regular, predetermined intervals.
・Condition-Based Maintenance: The operating condition of the machinery is monitored, and maintenance is performed before abnormalities occur.
(2) Reactive Maintenance: Repairs are carried out when a failure occurs, and measures are taken to prevent recurrence.
(3) Improvement Maintenance: Equipment is modified or improved to prevent recurrence after a failure.
By implementing these maintenance activities, it is possible not only to improve the productivity of a factory but also to minimize the risk of production stoppages due to failures.
2.Specific Methods in Equipment Maintenance
Daily inspections and periodic inspections are crucial for continuously monitoring the condition of machinery and preventing failures. Specifically, by establishing clear criteria and methods for inspection items, and having managers verify the implementation of these checks, the healthy condition of equipment can be maintained.
In recent years, more companies have started utilizing “Equipment Maintenance Management Systems” to optimize inspections and reduce workload. These systems enable the automation of timely maintenance planning, taking into account past failure records and costs.
Furthermore, predictive maintenance is a method that utilizes vibration sensors and ultrasonic sensors to detect early signs of failure and respond proactively. In particular, ultrasonic sensors can detect abnormalities earlier than vibration sensors, making it an effective measure for failure prevention. Additionally, AI diagnostic tools have become increasingly important as part of technological innovations to address the shortage of skilled technicians.
3.Reactive Maintenance Response
Reactive maintenance is a method in which repairs are carried out after machinery has failed, and measures are implemented to prevent recurrence. When machine failures occur, the following flow is typically followed for handling them.
- Investigation of Failure Cause: First, identify the cause of the failure and utilize past troubleshooting records to organize the situation.
- Assessment of Part Replacement Feasibility: Check the availability of spare parts and whether the same model is used in other factories to determine if part replacement is possible.
- Emergency Meetings with Stakeholders: Quickly discuss repair methods and arrangements for resuming operations with stakeholders.
- Quickly discuss repair methods and arrangements for resuming operations with stakeholders.: Summarize the details of the failure and the actions taken in a standardized format to ensure the seamless handover of information to the next shift. In reactive maintenance, where prompt and accurate response is required, it is especially important to manage with limited resources, such as during night shifts. Additionally, since production stoppages can lead to significant sales opportunity losses, the early restoration of equipment failures is a critical issue for companies.。
4.Important Factors for Reducing Downtime
To reduce downtime, it is essential to set clear annual targets when establishing KPIs. Organize the previous year’s data on downtime hours and incidence, categorize completed and ongoing recurrence prevention measures, and set target numbers accordingly.
Additionally, analyzing equipment failure records from the past three years and creating a preventive maintenance plan that considers cost-effectiveness is effective. Regular operation (weekly is desirable) of an Equipment Failure Reduction Committee is also important. Through these weekly meetings, the committee verifies failure records, cause analysis, and the progress of recurrence prevention measures. It is crucial for the manufacturing department, facility management department, maintenance department, quality control department, and cost management department to work together as a unified factory to implement measures aimed at reducing failures.
5.Importance of Human Resource Development
Human resource development is essential for equipment maintenance. In particular, it is necessary to develop the ability to detect abnormalities through practical experience in addition to technical knowledge. To notice abnormalities, it is necessary to know the “normal” state of equipment and machinery and be sensitive to changes from that state.
Troubleshooting, data analysis, and logical thinking skills are also important for engineers. Communication skills are critical when forming technical hypotheses about detected differences and promptly reporting them to supervisors.
Currently, many manufacturing industries face challenges due to a shortage of engineers, making the transfer of technology from veteran employees to younger employees a crucial theme. Encouraging growth through accumulated experience and ultimately developing personnel who can excel as “true engineers” is a significant factor in the success of equipment maintenance activities.
Especially, engineers who can lead the Equipment Failure Reduction Committee and proactively tackle the improvement of issues on the ground are essential for ensuring the stable operation of the site. It is no exaggeration to say that their efforts are crucial for maintaining stability and efficiency in operations.
The consultant who wrote this column

Tomohiro Suzuki
Field Improvement Consultant / Former Japan Tobacco Inc. Employee – Technology Development Department and Manufacturing Department
With extensive experience in new process development, safety management, quality improvement, cost reduction, delivery management, and human resource development.
▼For inquiries about factory assessments, please contact us here.
Inquiry for the factory diagnosis